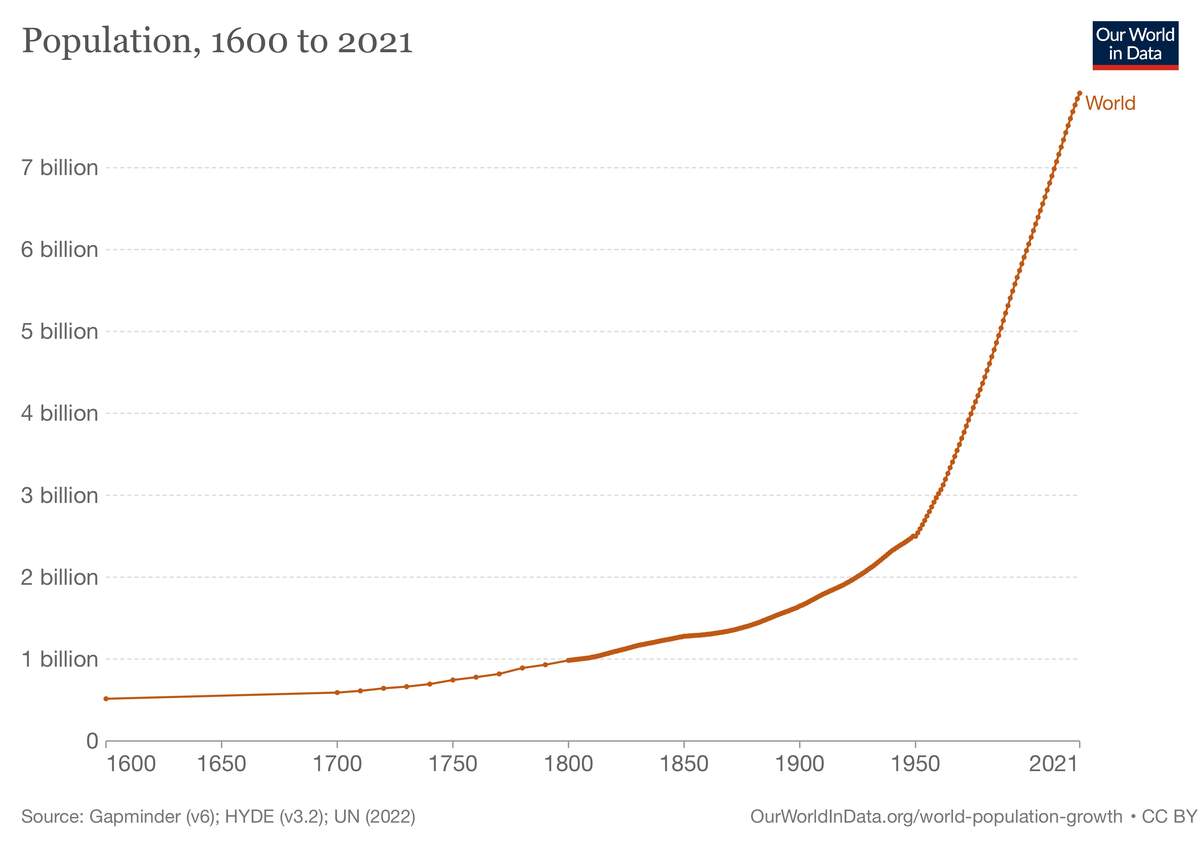
On November 15, the United Nations (UN) reported that the number of people on Earth had grown to eight billion (8,000,000,000). That came just 11 years after the world reached seven billion people. The world faces challenges ahead as the population continues to grow.
The world’s population – the number of people on the planet – has grown rapidly over the last 200 years. In 1805, for the first time ever, the Earth had a billion people on it. It took over 100 years for that number to double to two billion. In less than 50 years, it had doubled again to four billion. Now, again in less than 50 years, the number has doubled once more to eight billion.
(Source: [CC BY 4.0], OurWorldInData.org.)
The World’s Population
The world’s population number isn’t exact, since people are dying and being born all the time. Instead, the number is an estimate based on the current populations of countries around the world and the rate at which those numbers are growing.
How fast local populations are growing depends a lot on where you are in the world. Typically, as countries become richer, their population growth slows. In some countries, like Japan, the number of people is actually shrinking. The greatest population growth these days is found in Asia and Africa.
Currently, China, with a population of 1.4 billion, is the country with the most people. That’s expected to change in the next year, when experts say India will pass China as the country with the world’s largest population. Other countries where rapid growth is expected through 2050 are the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines, and Tanzania.
😕
This image has not been loaded because of your cookie choices. To view the content, you can accept 'Non-necessary' cookies.
Currently, China, with a population of 1.4 billion, is the country with the most people. That’s expected to change in the next year, when experts say India will pass China as the country with the world’s largest population. Above, a busy market in Bangalore, India.
As its population grows, the world faces the increased challenges of how to feed, educate, and meet the medical needs of everyone on the planet. This is made more difficult because populations are growing most quickly in poorer countries.
To care for that many people, humans will need to change they way they use the world’s land, water, and other resources. Some people see the world’s population growth as a climate problem. Adding more people to the world, they say, will only make global warming worse.
But experts say it’s not that simple. Most of the countries where populations are growing quickly create just a tiny fraction of the pollution driving the climate crisis. The real problem is the energy used and pollution created by richer countries where population growth is much slower.

(Source: Vijay8808 [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons.)
For example, the US state of South Dakota has just 895,000 people. Tanzania, one of the fastest-growing countries, has a population of about 61,740,000. Both produce about the same amount of emissions each year.
One reason the world’s population is growing is that, in general, people are living longer than they used to. In some countries, this could present a challenge, with more and more older people, but fewer young people to support them.
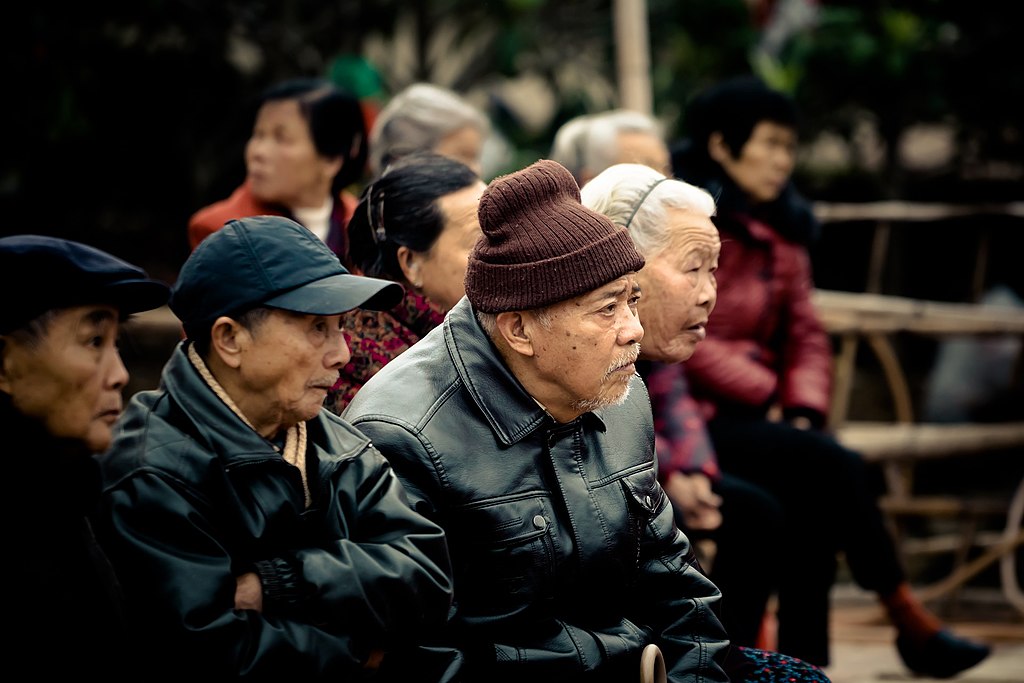

(Source: 志涛 张 [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons.)
Overall, even though the world’s population continues to grow, it’s growing more slowly than before. It’s impossible to say exactly what will happen in the future, but the rate of growth is expected to keep slowing down. By 2050, the UN expects the Earth to have about 9.7 billion people. Experts say that by 2100, the planet’s population could level off at about 10.4 billion people.
